카카오톡 상담 ID : myuhak, Tel : 070 4044 0545, 이메일 : info@myuhak.com
일반적으로 어학기관의 레벨은 6단계로 레벨 분화가 되어 있습니다. 이것에 대한 기준을 명확하게 보기 위해서 살펴봐야 할 것이 CEFR 기준입니다. 아래의 위키 피디어 내용을 참조하시고 A1부터 C2까지 총 6단계에 대한 기본사항을 이해하시면 어학연수에 도움이 되실 것입니다.
CEFR(Common European Framework of Reference for Languages)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, Teaching, Assessment, abbreviated as CEFR or CEF, is a guideline used to describe achievements of learners of foreign languages across Europe and, increasingly, in other countries (for example, Colombia and the Philippines). It was put together by the Council of Europe as the main part of the project "Language Learning for European Citizenship" between 1989 and 1996. Its main aim is to provide a method of learning, teaching and assessing which applies to all languages in Europe. In November 2001 a European Union Council Resolution recommended using the CEFR to set up systems of validation of language ability. The six reference levels (see below) are becoming widely accepted as the European standard for grading an individual's language proficiency.
Development
In 1991 the Swiss Federal Authorities held an Intergovernmental Symposium in Rüschlikon, Switzerland, on "Transparency and Coherence in Language Learning in Europe: Objectives, Evaluation, Certification". This symposium found that a common European framework for languages was needed to improve the recognition of language qualifications and help teachers co-operate, eventually leading to improved communication and cooperation among language teachers in Europe.
As a result of the symposium, the Swiss National Science Foundation set up a project to develop levels of proficiency, to lead on to the creation of a "European Language Portfolio" - certification in language ability which can be used across Europe.
A preliminary version of the Manual for Relating Language Examinations to the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) was published in 2003. This draft version was piloted in a number of projects, which included linking a single test to the CEFR, linking suites of exams at different levels, and national studies by exam boards and research institutes. Practitioners and academics shared their experiences at a colloquium in Cambridge in 2007 and the pilot case studies and findings were published in Studies in Language Testing (SiLT). The findings from the pilot projects then informed the Manual revision project during 2008/09.
Theoretical background
The CEFR adopts an action-oriented approach that, according to Carlos César Jiménez of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, can be traced back to theoretical proposals made by philosophers of language such as Ludwig Wittgenstein in the 1950s and sociolinguists such as Dell Hymes. The approach regards language users as social agents who develop general and particular communicative competences while trying to achieve their everyday goals.
The CEFR divides general competences in knowledge (descriptive knowledge), skills, and existential competence with particular communicative competences in linguistic competence, sociolinguistic competence, and pragmatic competence. This division does not exactly match previously well-known notions of communicative competence, but correspondences among them can be made.
General and particular communicative competences are developed by producing or receiving texts in various contexts under various conditions and constraints. These contexts correspond to various sectors of social life that the CEFR calls domains. Four broad domains are distinguished: educational, occupational, public, and personal.
A language user can develop various degrees of competence in each of these domains and to help describe them the CEFR has provided a set of Common Reference Levels.
Common reference levels
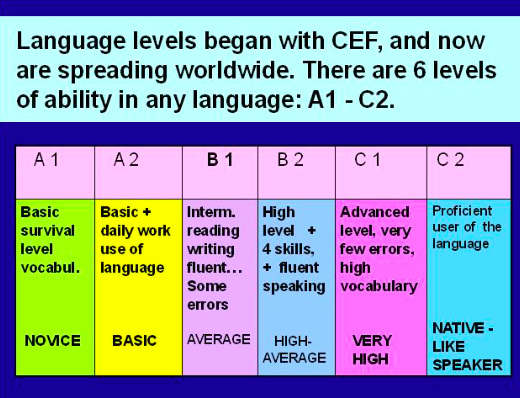
The Common European Framework divides learners into three broad divisions that can be divided into six levels; for each level, it describes what a learner is supposed to be able to do in reading, listening, speaking and writing. These levels are:
| level group | level group name | level | level name | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Basic User | A1 | Breakthrough or beginner |
|
| A2 | Way stage or elementary |
|
||
| B | Independent User | B1 | Threshold or intermediate |
|
| B2 | Vantage or upper intermediate |
|
||
| C | Proficient User | C1 | Effective Operational Proficiency or advanced |
|
| C2 | Mastery or proficiency |
|
These descriptors can apply to any of the languages spoken in Europe, and there are translations in many languages.
Rest of the world
The table below summarizes the correspondences between CEFR levels and common language proficiency scales around the world.
| Language (ISO 639-3) |
Certificate | A1 | A2 | B1 | B2 | C1 | C2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mul | UNIcert | UNIcert I | UNIcert II | UNIcert III | UNIcert IV | ||
| mul | TELC | A1 | A2 | B1 | B2 | C1 | C2 |
| cat | Catalan Language Certificates | Bàsic-A2 | Elemental-B1 | Intermedi-B2 | Suficiència-C1 | Superior-C2 | |
| cmn | Chinese Hanyu Shuiping Kaoshi(HSK) | HSK Level 3 | HSK Level 4 | HSK Level 5 | HSK Level 6 | - | - |
| cmn | Test of Chinese As A Foreign Language(TOCFL) (Taiwan) | TOCFL Level 1 | TOCFL Level 2 | TOCFL Level 3 | TOCFL Level 4 | TOCFL Level 5 | |
| cym | WJEC Defnyddio'r Gymraeg | Mynediad (Entry) | Sylfaen (Foundation) | Canolradd (Intermediate) | - | Uwch (Advanced) | Hyfedredd (Proficiency) |
| cze | Czech Language Certificate Exam (CCE) | CCE-A1 | CCE-A2 | CCE-B1 | CCE-B2 | CCE-C1 | - |
| dan | Prøve i Dansk (Danish Language Exam)[36] | Prøve i Dansk 1 | Prøve i Dansk 2 | Prøve i Dansk 3 | Studieprøven | ||
| deu | Goethe-Institut | Goethe-Zertifikat A1 Start Deutsch 1 |
Goethe-Zertifikat A2 Start Deutsch 2 |
Goethe-Zertifikat B1 Zertifikat Deutsch(ZD) |
Goethe-Zertifikat B2 Zertifikat Deutsch für den Beruf (ZDfB) |
Goethe-Zertifikat C1 Zentrale Mittelstufenprüfung |
Goethe-Zertifikat C2 - Großes Deutsches Sprachdiplom (GDS) Zentrale Oberstufenprüfung Kleines Deutsches Sprachdiplom |
| deu | TestDaF | TDN 3 — TDN 4 | TDN 4 — TDN 5 | ||||
| ell | Πιστοποίηση Ελληνομάθειας(Certificate of Attainment in Modern Greek) | Α1 (Στοιχειώδης Γνώση) |
Α2 (Βασική Γνώση) |
Β1 (Μέτρια Γνώση) |
Β2 (Καλή Γνώση) |
Γ1 (Πολύ Καλή Γνώση) |
Γ2 (Άριστη Γνώση) |
| eng | Anglia Examinations | Preliminary | Elementary | Intermediate | Advanced | Proficiency | Masters |
| eng | TrackTest | A1 (Beginner) | A2 (Elementary) | B1 (Pre-Intermediate) | B2 (Intermediate) | C1 (Upper-Intermediate) | C2 (Advanced) |
| eng | iTEP | 1-2 | 2.5-3 | 3.5 | 4-4.5 | 5-5.5 | 6 |
| eng | IELTS | 2.0 | 3.0 | 3.5-4.5 (3.5 is the margin) | 5.0-6.0 (5.0 is the margin) | 6.5-7.5 (6.5 is the margin) | 8.0-9.0 (8.0 is the margin) |
| eng | TOEIC | 60 - 105 (listening) 60 - 110 (reading) | 110 - 270 (listening) 115 - 270 (reading) | 275 - 395 (listening) 275 - 380 (reading) | 400 - 485 (listening) 385 - 450 (reading) | 490 - 495 (listening) 455 - 495 (reading) | |
| eng | Versant | 26-35 | 36-46 | 47-57 | 58-68 | 69-78 | 79-80 |
| eng | Duolingo English Test | ? | ? | 2.6 to 5.5 | 5.6 to 8.5 | 8.6 to 10.0 | ? |
| eng | TOEFL (IBT) | 8-12 (speaking) | 13-18 (speaking), 11-16 (writing) | 57 to 86 | 87 to 109 | 110 to 120 | 29-30 (reading) |
| eng | TOEFL ITP | 337 | 460 | 543 | 627 | ||
| eng | TOEFL Junior Standard | 225-245 (listening), 210-245 (language form), 210-240 (reading) | 250-285 (listening), 250-275 (language form), 245-275 (reading) | 290-300 (listening), 280-300 (language form), 280-300 (reading) | |||
| eng | City and Guilds | Preliminary | Access | Achiever | Communicator | Expert | Mastery |
| eng | NQF (UK Only) | Entry Level | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Levels 4-6 | Level 7-8 |
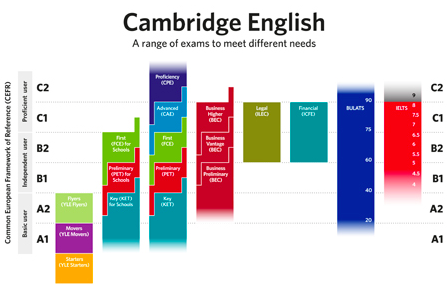
| eng | Cambridge exam | KET (45 to 59) | PET (45 to 59)/ KET Pass with Merit, Pass | FCE (45 to 59) / PET Pass with Merit, Pass / KET Pass with Distinction | CAE (45 to 59) / FCE grade B or C / PET Pass with Distinction | CPE (45 to 59) / CAE grade B or C / FCE grade A | CPE grade A, B or C / CAE grade A |
| eng | EXAMAGRAM | 143-245 | 246-428 | 429-579 | 572-714 | 715-858 | 859-1000 |
| eng | PTE Academic | 30 | 43 | 59 | 76 | 85ƒ | |
| eng | PTE General (formerly LTE) | Level A1 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 5 |
| eng | Trinity College London Integrated Skills in English (ISE) / Graded Examinations in Spoken English (GESE) / Spoken English for Work (SEW) | GESE 2 | ISE 0 GESE 3, 4 |
ISE I GESE 5, 6 SEW 1 |
ISE II GESE 7, 8, 9 SEW 2, 3 |
ISE III GESE 10, 11 SEW 4 |
ISE IV GESE 12 |
| eng | British General Qualifications | Foundation Tier GCSE | Higher Tier GCSE | GCE AS level / lower grade A-level | GCE A-Level (known as A2) | ||
| eus | IVAP-HAEE | HE 1 - IVAP-HAEE | HE 2 - IVAP-HAEE | HE 3 - IVAP-HAEE | HE 4 - IVAP-HAEE | ||
| eus | HABE | Lehenengo maila - HABE | Bigarren maila - HABE | Hirugarren maila - HABE | Laugarren maila - HABE | ||
| eus | EGA | Euskararen Gaitasun Agiria | |||||
| fin | YKI | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| fra | CIEP / Alliance française diplomas | TCF A1 / DELFA1 | TCF A2 / DELFA2 / CEFP 1 | TCF B1 / DELF B1 / CEFP 2 | TCF B2 / DELF B2 / Diplôme de Langue | TCF C1 / DALF C1 / DSLCF | TCF C2 / DALFC2 / DHEF |
| glg | Certificado de lingua galega (CELGA)[67] | CELGA 1 | CELGA 2 | CELGA 3 | CELGA 4 | CELGA 5 | |
| ita | CELI | Impatto | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| ita | CILS | A1 | A2 | Uno | Due | Tre | Quattro / DIT C2 |
| ita | PLIDA (Dante Alighieri Society diplomas) | PLIDA A1 | PLIDA A2 | PLIDA B1 | PLIDA B2 | PLIDA C1 | PLIDA C2 |
| jpn | Japanese-Language Proficiency Test(JLPT) | N5 | N4 | N3 | N2 | N1 | - |
| kor | Test of Proficiency in Korean (TOPIK) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 5 | Level 6 |
| nld | CNaVT - Certificaat Nederlands als Vreemde Taal (Certificate of Dutch as Foreign Language) | Profile tourist and informal language proficiency (PTIT) | Profile societal language proficiency (PMT) | Profile professional language proficiency (PPT), Profile language proficiency higher education (PTHO) | Profile academic language proficiency (PAT) | ||
| nld | Inburgeringsexamen (Integration examination for immigrants from outside the EU) | Pre-examination at embassy of home country | Examination in the Netherlands | ||||
| nld | Staatsexamen Nederlands als tweede taal NT2 (State Examination Dutch as second language NT2) | NT2 programma I | NT2 programma II | ||||
| nor | Norskprøver | Norskprøve 1 | Norskprøve 2 | Norskprøve 3 | Bergenstest | ||
| por | CAPLE | QECR | CIPLE | DEPLE | DIPLE | DAPLE | DUPLE |
| por | CELPE-Bras | Intermediate | Intermediate | Superior Intermediate | Superior Intermediate | Advanced | Superior Advanced |
| rus | ТРКИ – Тест по русскому языку как иностранному (TORFL – Test of Russian as a Foreign Language) | ТЭУ Элементарный уровень | ТБУ Базовый уровень | ТРКИ-1 (I Cертификационный уровень) (1st Certificate level) | ТРКИ-2 | ТРКИ-3 | ТРКИ-4 |
| spa | DELE | A1 | A2 | B1 (formerly "Inicial") | B2 (formerly "Intermedio") | C1 | C2 (formerly "Superior") |
| swe | TISUS | - | - | - | - | TISUS | - |
| swe | Swedex | - | A2 | B1 | B2 | - | - |
| AMCAD EFL | A1 | A2 | B1 | B2 | C1 | C2 | |
| ALTE level | Breakthrough level | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 5 | |
| ukr | UMI/ULF - Ukrainian as foreign language | UMI 1 | UMI 2 | UMI 3 | UMI 4 | UMI 5 | UMI 6 |